Temperature
the measure of how hot or cold a substance is relative
to another substance
Heat always flows from a substance with a higher temperature
to a substance with a lower temperature until both are at equilibrium.
Celsius, Kelvin & Fahrenheit
Temperatures
| SI Units |
Kelvin |
Room Temp = 295 K |
| Metric Units |
Celsius °C |
Room Temp = 22 °C |
| US Units |
Fahrenheit °F |
Room Temp = 72 °F |
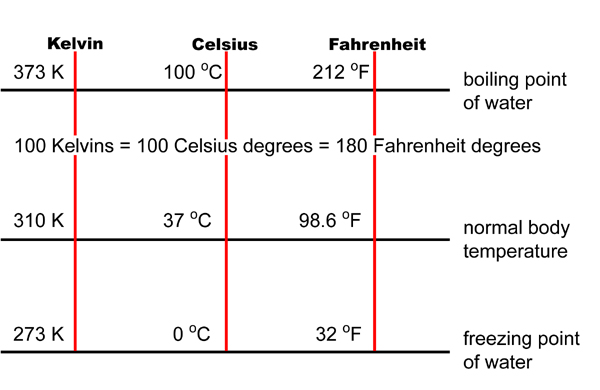 Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit
Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit
(180 °F from freezing point to boiling point ÷
100 °C + 32°):
or
TF
= 1.8 (TC) + 32°
Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius
(The derivation of a formula)
| TF |
= 1.8 (TC)
+ 32° |
| TF
- 32° |
= 1.8 (TC)
+ 32° - 32° |
| TF
- 32° |
= 1.8 (TC) |
|
So that
|
|
|
|
= TC |
Converting Celsius to Kelvin
(and vice-versa)
TK
= TC +273 or
TK – 273 = TC
(Remember that there is NO degree symbol (°) for Kelvin!)
How do temperatures in Fahrenheit,
Celsius, and Kelvin relate?
Practice Problems
Answer the following questions: |
|
| 1. |
The temperature of a room is set at 22°C.
If that temperature is lowered by 1°C, it can save as much as 5% in
energy costs. What should the temperature be set at in degrees Fahrenheit
to be 1°C lower than 22°C? |
|
|
| 2. |
When making homemade ice cream, rock salt
is used to chill the mixture. If the temperature drops to -11°C,
what is it in °F? |
|
|
| 3. |
In chemotherapy, temps up to 113°F are
used to destroy cancer cells. What is that temperature in degrees
Celsius? |
|
|
| 4. |
A child has a temperature of 103.6°F.
What is the temperature on a Celsius thermometer? |
|
|
|
|
|
|


