| Of all the changes that swept Europe in the sixteenth
and seventeenth centuries, the most widely influential was the Scientific
Revolution. It was during the Scientific Revolution that man
realized that there were laws that described how the world worked that
could be observed, measured, and used to understand the universe itself.
Causes of the Scientific Revolution
-
The development of new technology and scientific theories
became the foundation of the Scientific Revolution.
In the Middle Ages:
“Natural Philosophers” did not observe the natural world.
Instead, they relied on ancient authorities—the Bible, Aristotle, etc.—for
knowledge
Impact of the Renaissance
Renaissance humanists had access to newly discovered
texts of Ptolemy, Archimedes, and Plato—which disagreed with Aristotle
& the Bible
New Technology and Mathematics
careful observation, accurate measurements needed for
trade (like how much weight a ship could hold)
New Technologies
telescope & microscope
printing press
—readers could contemplate and comment
on written ideas
chronometer to measure time and calculate
longitude—
James Cook used the chronometer to map Australian
coast & chart Pacific Ocean
James Cook also discovered eating fresh fruits &
vegetables prevented scurvy, which helped sailors on long voyages
Mathematics
François Viète used letters to represent
unknown quantities
laid foundation for development of trigonometry
Simon Stevin, Flemish engineer, introduced decimal
system
John Napier invented table of logarithms
all this made calculations easier
Later scientists believed the secrets of the universe
were written in the language of mathematics.
REVIEW & DO
NOW
Answer the following questions in your spiral notebooks: |
| During the Middle Ages, would “natural philosophers”
base knowledge on observavtion of the natural world or rely on ancient
authorities?
Renaissance humanists had access to newly rediscovered
texts that disagreed with Aristotle and the Bible about the nature of the
world. Name one of these writers.
Name four new technologies developed during the later
Renaissance that helped spur scientific thinking.
Were mathematicians using letters to represent unknown
quantities during this time? |
What new technology did John Cook use to map out the
coastline of Australia and chart the Pacific Ocean?
Regarding the instrument John Cook used to map the coastline
of Australia, what function did it serve?
What did the printing press allow people to do that helped
initiate the Scientific Revolution?
Name something else going on in the time period are we
discussing now?].
Did the United States of America already exist during
this time? |
|
|
The Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was started by two books, both
published in 1543—
On the Revolution of Heavenly Orbs, by Nicolaus
Copernicus
and
On the Fabric of the Human Body, by Andreas Vesalius.
The printing press made the wider spread of ideas possible.
The Concept of the Universe in the Ancient World
 |
The Ptolemaic System
Ptolemy—100-168, CE,
greatest astronomer of antiquity.
The Almagest, circa 150 CE.
Using works of Ptolemy, Aristotle, and Catholic Church,
medieval astronomers constructed the Ptolemaic model of the universe. |
 |
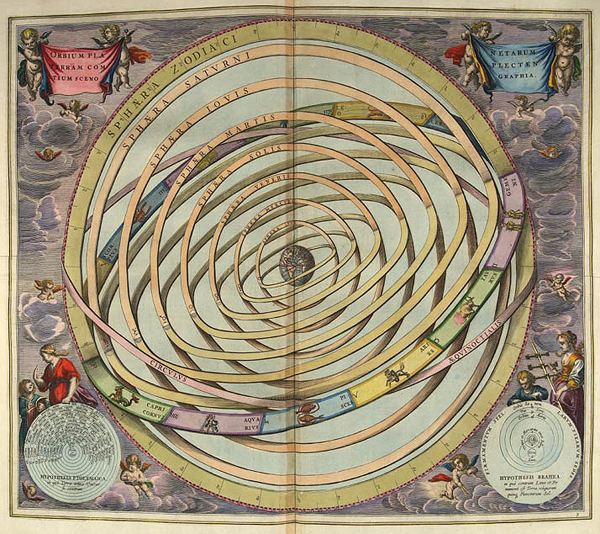 The Geocentric (Earth-Centered) Universe
The Geocentric (Earth-Centered) Universe
Ptolemaic System—
Earth is the center of the entire universe, unmoving,
with sun, the moon, planets, and stars going around it.
The universe was a series of concentric, solid crystalline
spheres, completely transparent, one inside the other, each in contact,
all revolving around the Earth, which sat fixed and unmovable in the center.
Heavenly bodies—sun, moon, planets, and stars—were pure
orbs of light, ethereal and without substance.
Copernicus and Kepler
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543)
Polish mathematician
May, 1543—On the Revolution of the Heavenly Orbs
Said the sun, not the Earth, was the center of the universe.
The Heliocentric Universe
The sun was the center of the universe, with Earth as
the third planet, and the moon orbiting Earth
The motion of the sun across the sky was because the
Earth turned on its axis as it revolved around the sun.
His test: If Earth and planets orbit the sun, then
we should see Venus go through phases like the moon.
Johannes Kepler (1571-1630)
German mathematician
Used detailed astronomical data obtained from Tycho Brahe
to derive his Laws of Planetary Motion.
1609: Astronomia nova
Kepler’s First Law of Planetary Motion said that the
orbits of the planets around the sun were elliptical.
Galileo's View of the Universe
Galileo Galilei saw farther than any man ever had before.
Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)
Italian mathematician and tutor to the de Medici family
First to use the telescope to look at the heavens
first to see: Mountains and craters on the moon
Jupiter’s moons
rings of Saturn
sunspots (and that the sun rotated)
the phases of Venus
Proved that heavenly bodies were composed of material
substance, like Earth
that the sun revolved on its axis
and proved that Earth and the planets orbit the sun
Galileo, 1610: The Starry Messenger
came into conflict with the Catholic Church
The Church ordered him to abandon his teaching and ideas.
By 1630s and 1640s, most astronomers accepted Galileo’s
ideas.
Still, astronomers could not explain the motion of the
universe: This was left to the greatest scientist of the Scientific
Revolution...
Newton’s View of the Universe
Isaac Newton explained how the heliocentric model of
the universe worked.
Isaac Newton
Born December 25, 1642 – Died March 20,1726
1687: Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy
Defined the three Laws of Motion
1. Every object in motion will remain in motion,
and every object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced
force.
2. The force of a moving object is equal to the
mass of the object times its acceleration:
F = ma
3. For every action there is an equal and opposite
reaction.
Invented calculus
Demonstrated that white light was made up of the colors
of the rainbow
Discovered gravity
Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
explains why the planets continue in elliptical orbits
every object in the universe is attracted to every other
object by a force called gravity
this law explains all motion in the universe
The Force of Gravity between two objects is a funtion of the product
of their two masses divided by the square of the distance between them,
multiplied by a universal gravitational constant.
F = G (M1 x M2)
/ d2
Breakthroughs in Medicine
In the Middle Ages, medicine was dominated by the works
of Galen, a physician from the First Century, CE.
Because he based his work on the anatomy of animals,
he was often wrong.
He believed the liver moved blood through the body.
Andreas Vesalius (1514-1564)
1543: On the Fabric of the Human Body
an anatomy text which used actual human bodies for reference
University of Padua in Italy
William Harvey (1578- 1657)
English physician
1628: On the Motion of the Heart and Blood in
Animals
Showed that the heart pumped blood, not the liver
also showed that the same blood flows through the veins
and arteries, making a complete circuit through the body
Breakthroughs in Chemistry
Robert Boyle (1627-1691)
Irish chemist
1661: The Sceptical Chymist: or Chymico-Physical
Doubts & Paradoxes
New definition of element—a substance which cannot be
broken down into simpler substances
Boyle’s Law: For a fixed amount of an ideal gas
kept at a fixed temperature, P (pressure) and V (volume) are inversely
proportional.
Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794
French chemist—Father of Modern Chemistry
1789: Elements of Chemistry
Disproved phlogiston theory
Invented system of naming elements and symbols
Identified oxygen and hydrogen and formula of water
Decapitated during French Revolution
REVIEW & DO
NOW
Answer the following questions in your spiral notebooks: |
| What two books started the Scientific Revolution?
What does geocentric universe mean?
What does heliocentric universe mean?
Which one did the Catholic Church say was true?
Who was the First Century Greek philosopher who taught
the geocentric model of the universe?
Who was the Renaissance mathematician who proposed the
heliocentric model of the universe?
Who was the German mathematician who first recognized
the orbits of the planets were elliptical and not circular?
Who was the first person in human history to see the mountains
and craters on the moon, the phases of Venus, that Jupiter had moons, and
that Saturn had rings? |
How did he do this?
Galileo’s observations disproved one aspect of Ptolemy’s
universe by showing for the first time which characteristic of heavenly
bodies?
Who discovered gravity, the laws of motion, the nature
of light, and invented calculus?
Who wrote the first accurate book on human anatomy?
How did he do this?
Who discovered that blood completes a circuit through
the body?
Who proposed that elements were substances that cannot
be broken down into simpler substances?
Who first discovered oxygen, hydrogen, and the formula
of water? |
|
|
Women's Contributions
-
Women scientists faced obstacles to practicing what they
had learned.
Margaret Cavendish
Observations on Experimental Philosophy
Argued that understanding of Nature was not the same
as mastery of nature.
Maria Winklemann
In Germany between 1650 and 1710, 14% of all astronomers
were women.
Maria Winkleman received her training from a self-taught
astronomer. She married Prussia's foremost astronomer, Gottfried
Kirch, and became his assistant. She made original contributions
to astronomy on her own, including the discovery of a comet.
However, after the death of her husband, she was unable
to obtain a post at the Berlin Academy, because the members feared it would
set a bad example to hire a woman.
REVIEW & DO
NOW
Answer the following questions in your spiral notebooks: |
| What was Margaret Cavendish's argument about science? |
What percent of all German astronomers were women? |
|
|
Philosophy & Reason
-
Scientists came to believe that reason was the chief source
of knowledge.
Descartes & Rationalism
René Descartes (1596-1650)
17th Century French philosopher
1637: Discourse on Method
First Principle: “I think, therefore I am”
Created Cartesian coordinates (x,y)
The Father of modern rationalism
Rationalism
The system of thought based on the belief that reason
is the chief source of knowledge.
Francis Bacon and the Scientific Method
What is the best way to understand the physical world?
Scientific Method
A systematic procedure for collecting and analyzing evidence.
From observing natural events, scientists propose possible
explanations for observed phenomena, then use experiments and observation
to test these hypotheses and arrive at a better understanding of the natural
world.
The Scientific Method is crucial to the evolution of science
because it enables knowledge to be added to our understanding of the natural
world and enables that knowledge to be revised and improved as new evidence
becomes available.
Francis Bacon (1561-1626)
English philosopher
1620: Novum Organum Scientiarum (New
Instrument of Science)
believed science should not rely on ancient authorities
but should use inductive reasoning to learn about nature.
First, free their minds of opinions that might distort
the truth—
Then, start with detailed facts and proceed toward general
principles
Inductive Reasoning
Inductive reasoning makes broad generalizations from
specific observations, going from the general to the particular.
REVIEW & DO
NOW
Answer the following questions in your spiral notebooks: |
| Which philosopher is noted for his statement “I think,
therefore I am”?
What is rationalism?
What is the systematic procedure for collecting and analyzing
evidence? |
Who was the person who developed the scientific method?
What is inductive reasoning? |
|
|
|





