-
The number of protons determines the identity of the atom.
-
The number and arrangement of electrons determines an
atomís physical and chemical properties.
All electrons in an atom possess energy,
but not all electrons have the same level of energy.
Energy Levels
The ascending levels of energy around a nucleus in
which electrons occur
The number representing the energy level of the
electron is called the Principle Quantum Number (n).
-
Of the elements known today, there are seven energy
levels (n = 1 to n = 7), with the seventh being
the highest.
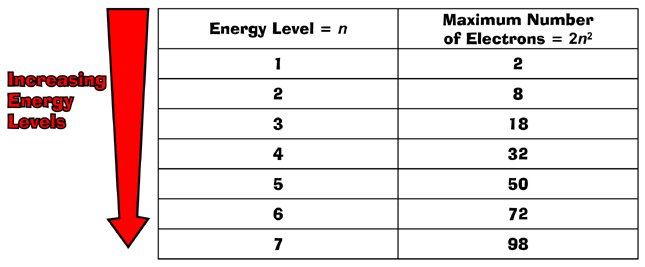
Each principal energy level can contain up to a maximum
2n2 electrons.
Thus, the first level can contain up to 2 electrons, 2(12)
= 2;
the second up to 8 electrons, 2(22)
= 8;
the third up to 18, 2(32)
= 18;
and so on.
Electron Level Arrangements
The electron level arrangement gives the number of
electrons in each energy level.
The arrangement of the electrons in an atom can be determined
from its position on the periodic table.
Electrons and their arrangements around the nucleus determines
the chemical properties of an element.
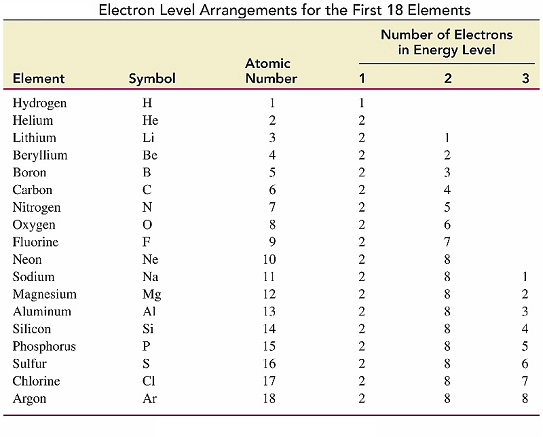
Example:
Sulfur, S, is in Period 3, which corresponds to Energy
Level 3.
.
Therefore, it has
-
two electrons in the first row,
-
eight electrons in the second
-
six electrons in the third.
The electron level arrangement for sulfur would be
written as 2, 8, 6.
What are the energy levels of
an atom?
Practice Problems
Answer the following questions: |
|
| 1. |
What determines an atom's physical and chemical
properties? |
|
|
| 2. |
What are the energy levels of an atom? |
|
|
| 3. |
What does the Principle Quantum Number,
n,
of an electron represent? |
|
. |
|
What would the formula 2n2
tell you about n? |
|
. |
|
What would be the maximum number of electrons in the
third
energy level of an atom? |
|
|
| 4. |
What do electron level arrangements
tell you? |
|
|
| 5. |
Write the electron level arrangement for
each of the following: |
|
.
| a) oxygen |
b) chlorine |
c) neon |
d) argon |
| . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6. |
What element has the electron level arrangement
of 2, 8, 2? |
|
|
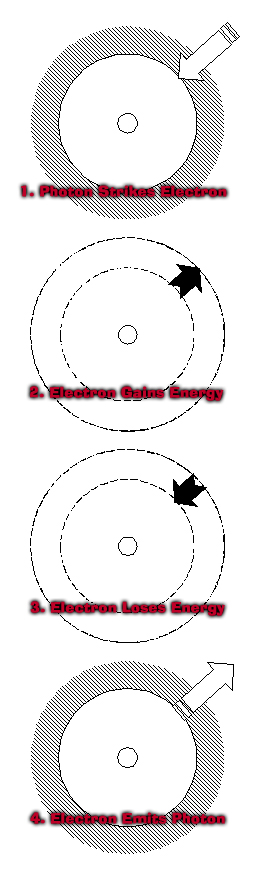
| Energy Level Changes
Photon
a discreet packet of energy without mass
that travels at the speed of light, with the properties
of both a particle and a wave
1. When a photon strikes an electron,
the energy level of the electron is raised
in correspondence to the energy of the photon.
The electron retains this extra energy
only temporarily.
Eventually, the electron
loses this extra energy.
2. When the electron goes back
to its normal energy level,
it emits a photon
equal to the amount of energy it loses.
When the energy of this photon
is within the visible range,
we see it as a color.
This is how things have the colors we see. |
|
How can photons affect the energy
level of the electron?
Practice Problems
Answer the following questions: |
|
|
|
|
| 2. |
What happens when a photon strikes an electron? |
|
|
| 3. |
Is the energy a photon transfers to an electron
permanent? |
|
|
| 4. |
What happens when an electron returns to
its original energy level? |
|
|
|
| Sources: CHEMISTRY - an Introduction to General, Organic, &
Biological Chemistry, Prentice Hall CHEMISTRY, Modern CHEMISTRY,
CHEMISTRY
- the Central Science, and Principles & Applications of CHEMISTRY |


