-
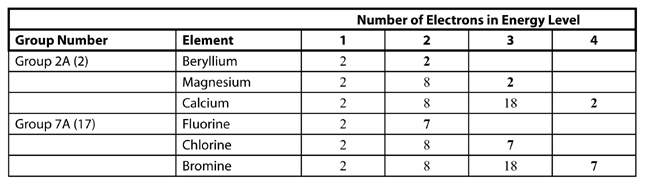
The electron level arrangement of atoms are an important
factor in the physical and chemical behavior of the elements.
Valence Electrons
electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom
Group Numbers 1A – 8A
designations at the top of each group of representative
elements that indicates the number of valence electrons
What is one of the most important
factors in the physical and chemical behavior of the elements?
Practice Problems
Answer the following questions: |
|
| 1. |
What are valence electrons? |
|
|
| 2. |
Using the Periodic Table, write the Group
Numbers and the number of valence electrons for the following elements: |
|
.
| a) sodium |
b) sulfur |
c) silicon |
d) indium |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
| 3. |
What is the group number, name, and symbol
of the element with atoms that have five valence electrons in the 3rd energy
level? |
|
|
Electron-Dot Symbols (a.k.a.
Lewis Structures)
the representation of an atom that shows valence electrons
as dots around the symbol of an element
1-4 valence electrons are arranged by single dots (added
clockwise)
more than 4 valence electrons & dots begin to pair
up.

What electrons are depicted in
Electron-Dot Symbols?
Practice Problems
Answer the following questions: |
|
| 1. |
Write the electron-dot symbol for each of
the following elements: |
|
.
| a) bromine |
b) iodine |
c) indium |
d) argon |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
| 2. |
What is the electron-dot symbol for phosphorus? |
|
. |
|
What group is it in? |
|
|
| 3. |
What is the electron-dot symbol for antimony
(Sb*)? |
|
. |
|
What group is it in? |
.
* Sb from stibium, the ancient name for antimony
sulfide, Sb2S3. |
|
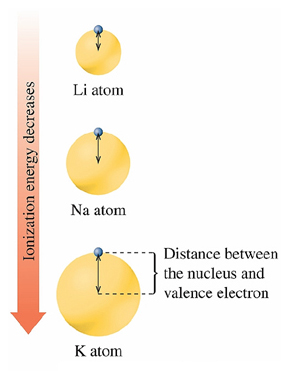
Atomic Size
measured by the
Atomic Radius
the distance from the nucleus
to the valence electrons
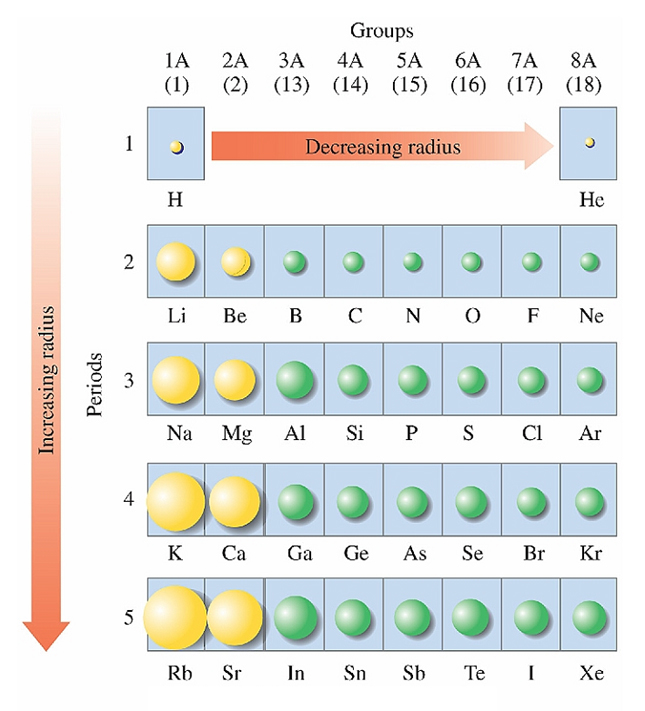
On the periodic table,
atomic size tends to
Increase going down the column
Decrease going across the rows from left to
right.
|
|
|
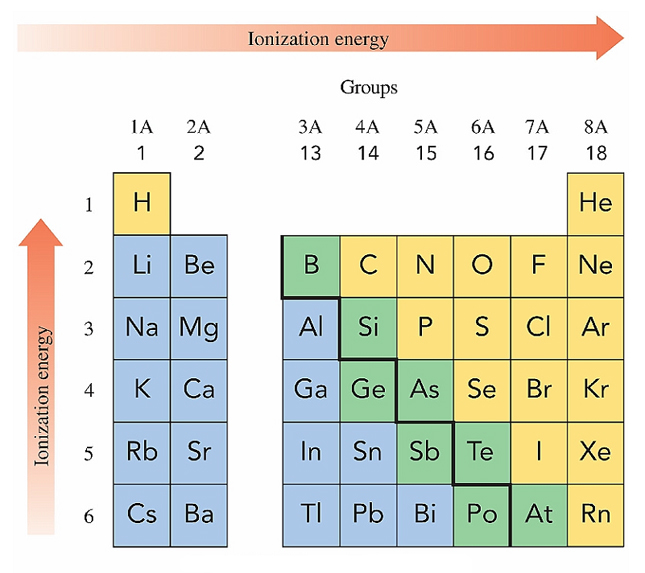
Ionization Energy
the energy needed to remove the least tightly bound
electrons from an atom in the gaseous state
On the periodic table, ionization energy tends to
decrease going down the column and
increase going across the rows from left to right.
Ionization energy is low for metals, high for non-metals.
Electronegativity
Ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom
is in a compound
Trends in electronegativity
are equivalent to ionization energy.
What are the trends in Atomic
Size, Ionization Energy, & Electronegativity?
Practice Problems
Answer the following questions: |
|
| 1. |
What is the atomic radius? |
|
|
|
|
| 2. |
Do the valence electrons get closer to the
nucleus or farther away as you go down the Group? |
|
|
| 3. |
Do the valence electrons get closer to the
nucleus or farther away as you go across the Period from left to right? |
|
|
| 4. |
What is ionization energy? |
|
|
| 5. |
Indicate the element in each set that has
the higher ionization energy and explain your choice: |
|
.
| a) H, K, or Na |
b) Mg, Si, or Cl |
c) F, N, or C |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
| 6. |
Explain the relationship between the size
of the atom and its ionization energy. |
|
|
|
|
| 7. |
Arrange Sn, I, and Sr in order of increasing
ionization energy. |
|
|
|
|
| 8. |
What is Electronegativity? |
|
|
| 9. |
Arrange Sn, I, and Sr in order of increasing
atomic radius. |
|
|
|
|
|
| Sources: CHEMISTRY - an Introduction to General, Organic, &
Biological Chemistry, Prentice Hall CHEMISTRY, Modern CHEMISTRY,
CHEMISTRY
- the Central Science, and Principles & Applications of CHEMISTRY |


